Print this page
view more examples
Topic: Pythagoras' Theorem (Higher - Unit 3)
| Specification References: G2.1h G2.1h Use Pythagoras’ theorem. Extend Pythagoras’ theorem to use in 3D. |
Candidates should be able to:
- understand, recall and use Pythagoras' theorem in 2D, then 3D problems
- investigate the geometry of cuboids including cubes, and shapes made from cuboids, including the use of Pythagoras' theorem to calculate lengths in three dimensions
Notes
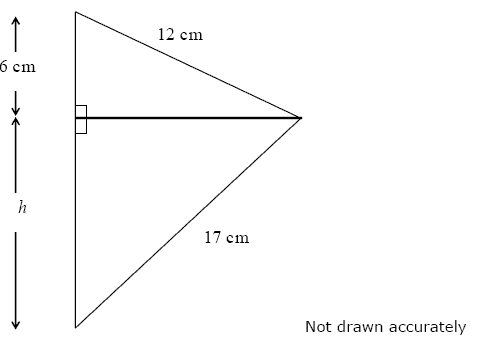
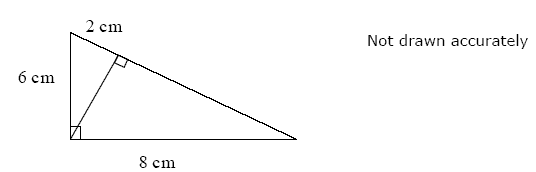
Questions may be set in context, for example, a ladder against a wall, but questions will always include a diagram of a right angled triangle with two sides marked and the third side to be found.
Quoting the formula will not gain credit. It must be used with appropriate numbers,
e.g. x2 = 72 + 82, x2 = 122 - 92 or x2 + 92 = 122
In three dimensions candidates should identify a right-angled triangle that contains the required information and then use Pythagoras' theorem (or trigonometry) to solve the problem. The use of the rule 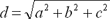 is not required as problems will always be solvable using a combination of triangles.
is not required as problems will always be solvable using a combination of triangles.
Example
- Find the length of the diagonal AB in the cuboid with dimensions 9cm, 40cm and 41cm.
(Diagram given.)
view more examples