Print this page
view more examples
Topic: Properties of Angles and Shapes (Higher - Unit 3)
| Specification References: G1.2 G1.2 Understand and use the angle properties of parallel and intersecting lines, triangles and quadrilaterals. |
Candidates should be able to:
- understand and use the angle properties of parallel lines
- recall and use the terms, alternate angles, and corresponding angles
- work out missing angles using properties of alternate angles and corresponding angles
- understand the consequent properties of parallelograms
- understand the proof that the angle sum of a triangle is 180o
- understand the proof that the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the interior angles at the other two vertices
- use angle properties of equilateral, isosceles and right-angled triangles
- use the angle sum of a quadrilateral is 360o
Notes
Candidates should be aware that colloquial terms such as ‘F angles’ or ‘Z angles’ should not be used.
Candidates should know the names and properties of isosceles, equilateral, right-angled and scalene triangles.
Examples
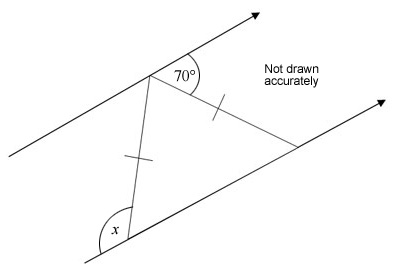
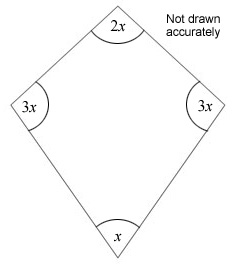
Work out the size of x.
You must explain any properties that you have used to obtain your answer.
view more examples